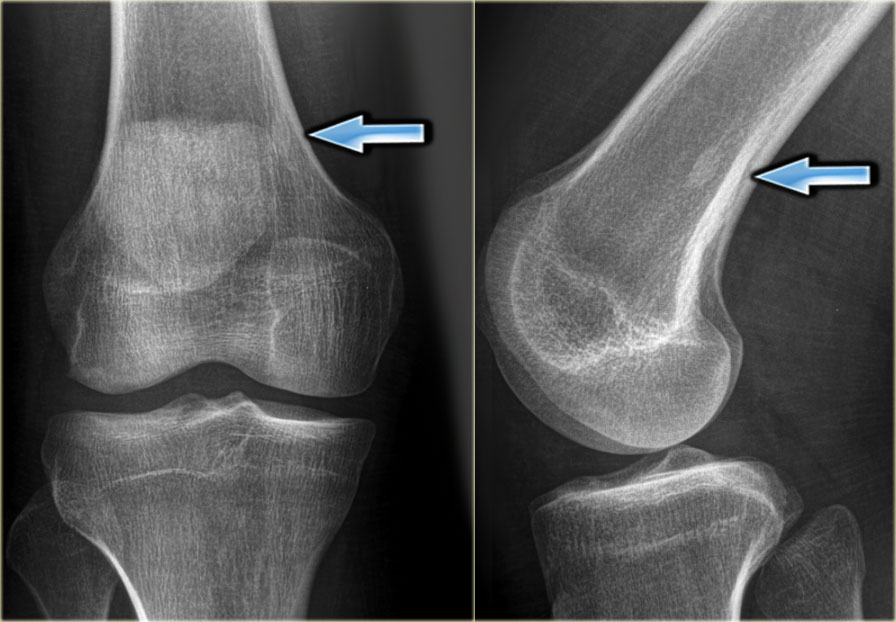
What Is Sclerosis Of The Bone. Sclerotic lesions are often seen in long bones but can be seen in most if not all bones of the body. Osteopetrosis which is also called Marble bone disease and Albers-Schonberg disease is an inherited condition that is characterized by elevated bone density. Subchondral sclerosis is the hardening of the bone just below the cartilage surface. Lesions should not be painful unless dysplasia is widespread with bowing deformity and pathologic fractures.
Sclerosis from Greek σκληρός sklērós hard is the stiffening of a tissue or anatomical feature usually caused by a replacement of the normal organ-specific tissue with connective tissue. Subchondral sclerosis is the hardening of the bone just below the cartilage surface. Bone reacts to its environment in two ways either by removing some of itself or by creating more of itself. These are specialized cells that. The structure may be said to have undergone sclerotic changes or display sclerotic lesions which refers to the process of sclerosis. Lesions of the medullary.
Sclerosis of a bone is a condition in which the bone itself thickens due to excessive calcium deposits.
Sclerosis when describing bone is defined as a pathologic thickening of the bone. Osteopetrosis which is also called Marble bone disease and Albers-Schonberg disease is an inherited condition that is characterized by elevated bone density. If the disorder it is reacting to is rapidly progressive there may only be time for retreat defense. Subchondral sclerosis is common in the bones found at the. Sclerosis from Greek σκληρός sklērós hard is the stiffening of a tissue or anatomical feature usually caused by a replacement of the normal organ-specific tissue with connective tissue. Sclerosis of subchondral bone which is the layer of bone just below the cartilage is often observed in people diagnosed with osteoarthritis.
