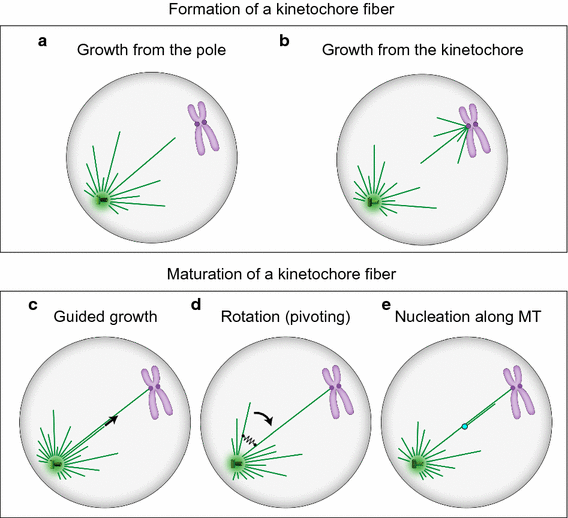
What Is Kinetochore Fibers. The functions of these complexes are to bind microtubules of the spindle bundle and depolarize them during the cell division. Together our data reveal that kinetochore-driven K-fiber formation is a major mechanism that contributes toward spindle assembly during normal mitosis in centrosomal cells. However integration of these kinetochore-organized K-fibers into the common spindle is facilitated by the centrosomes via a dynein-dependent search-and-capture. Kinetochore-driven outgrowth of microtubules is a central contributor to kinetochore fiber maturation in crane-fly spermatocytes.

Identical joined copies of a single chromosome are known as sister chromatids. Find an answer to your question What are kinetochore fibers. Yet how it remodels under force remains poorly. The functions of these complexes are to bind microtubules of the spindle bundle and depolarize them during the cell division. Kinetochore is a disc-shaped protein complex present in the centromere region of a chromosome which is in the mitotic or meiotic division. Kinetochore fibers extend from the kinetochore region and attach chromosomes to microtubule spindle polar fibers.
During anaphase kinetochore fibers shorten by depolymerization at the kinetochore and at the pole thereby segregating sister chromatids towards the opposite spindle poles Asbury 2017.
Polar microtubules interdigitate at the spindle midzone and push the spindle poles apart via motor proteins. Cell division is one of the most fundamental processes in the living world. Each chromosome has a kinetochore. Kinetochore is a disc-shaped protein complex present in the centromere region of a chromosome which is in the mitotic or meiotic division. What happens in prophase. Kinetochore fibers and spindle polar fibers work together to separate chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis.