
What Is Involved In Enzyme Catalysis. Usually this covalent bond is formed by the reaction of a nucleophilic group on the catalyst with an electrophilic group on the. Circles C and D represent substrate-binding groups on the enzyme that are essential for catalytic activity. Like enzymes themselves coenzymes are not changed during catalysis. COVALENT CATALYSIS The process of covalent catalysis involves the formation of a covalent bond between the enzyme and one or more substrates.
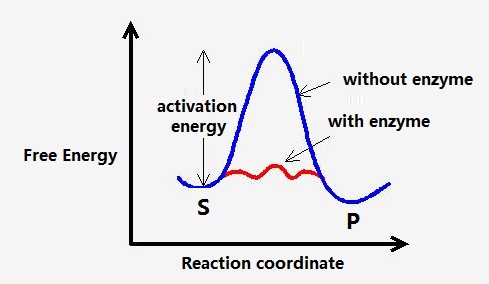
Some of these include. In a catalytic pathway the reaction takes a different course than it would on its own. Enzymes are proteins that accelerate biochemical transformations by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Usually this covalent bond is formed by the reaction of a nucleophilic group on the catalyst with an electrophilic group on the. They are similar to other chemical catalysts in many ways. In the absence of enzymatic catalysis most biochemical reactions are so slow that they would not occur under the mild conditions of temperature.
Enzyme Catalysis Introduction.
The acid- and base-catalyzed reactions at high and low pH are not directly relevant to catalysis by enzymes. Strategies in Enzyme Catalysis Once a substrate has been bound it is the enzymes job to quickly transform the substrate into product. Mechanism of Acid-base Catalysis. For example the enzyme hexokinase closes like a clamshell when it binds glucose. Pyridoxal 5-phosphate PLP cofactor derived from Vitamin B6 is widely distributed in nature and has significant latitude in catalytic diversity. Enzymes can destabilize bonds within the substrate.