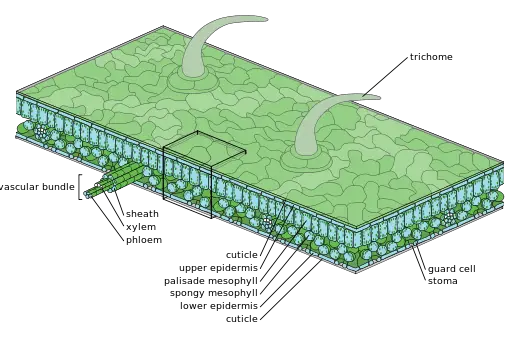
Multiple Epidermis Plants Examples. Prevention of mechanical injury and invasion by parasite fungi. The epidermis in plants is a layer of cells that usually covers the roots stems leaves and flowers of plants. Trichomes on plants are epidermal outgrowths of various kinds. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium particularly a stratified squamous epithelium The word epidermis is derived through Latin from Ancient Greek epidermis itself from Ancient Greek.

In most plants the epidermis is a single layer of cells set close together to protect the plant from water loss invasion by fungi and physical damage. The protoderm cells divide anticlinally and in course of time uniseriate epidermis is formed. There is an upper and lower epidermis in the leaves. The role of the epidermis in plants are as follows. Vallisneria Hydrilla Eichhornia water hyacinth Wolffia Lemna etc. Exchange of gases and transpiration through stomata.
The terms emergences or prickles refer to outgrowths that involve more than the epidermis.
The role of the epidermis in plants are as follows. McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific Technical Terms 6E Copyright 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc. Transpiration photosynthesis protein synthesis while a tissue performs only a specific function. Many-layered or multiseriate epidermis usually called multiple epidermis is found in some organs like roots of orchids leaves of Ficus spp. For example the inhibition of cell division in the epidermis by expression of the cell cycle inhibitor Kinase Inhibitor Protein KIPRELATED PROTEIN1INHIBITOR1 OF CDC2 KINASE KRP1ICK1 under the control of the AtML1 promoter Bemis Torii 2007 resulted in small plants which had abnormally large epidermal cells. Example needed A common type of trichome is a hair.