Monetary Policy Great Recession. Expanding the money supply results in lower. The book outlines how Congress the executive branch and. Estimating the Macroeconomic Effects of a Spread Compression at the Zero Lower Bound Christiane Baumeistera and Luca Benatib aBank of Canada bUniversity of Bern We explore the macroeconomic effects of a compression in the long-term bond yield spread within the context of. The Fed is the nations central banking institution.
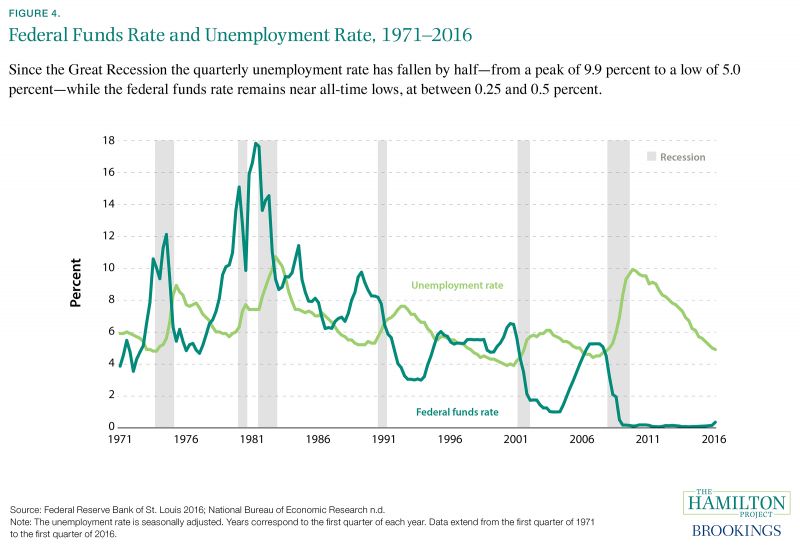
During the Great Recession the government used monetary and fiscal policy to regulate economical activities in order to stabilize the A period in which there is a reduction in the Gross Domestic Product GDP increase in unemployment and decline in the economy is called a recession. The over 4 percent decline in gross domestic product GDP was only reversed more than three years after the beginning of the recession. Download Citation On Sep 26 2020 Arkadiusz Sieroń published Monetary Policy after the Great Recession. Outside the box. Purchasing of security bonds and MBS. Confronting Policy Challenges of the Great Recession.
It is the bank for the government itself as well as for national commercial banks.
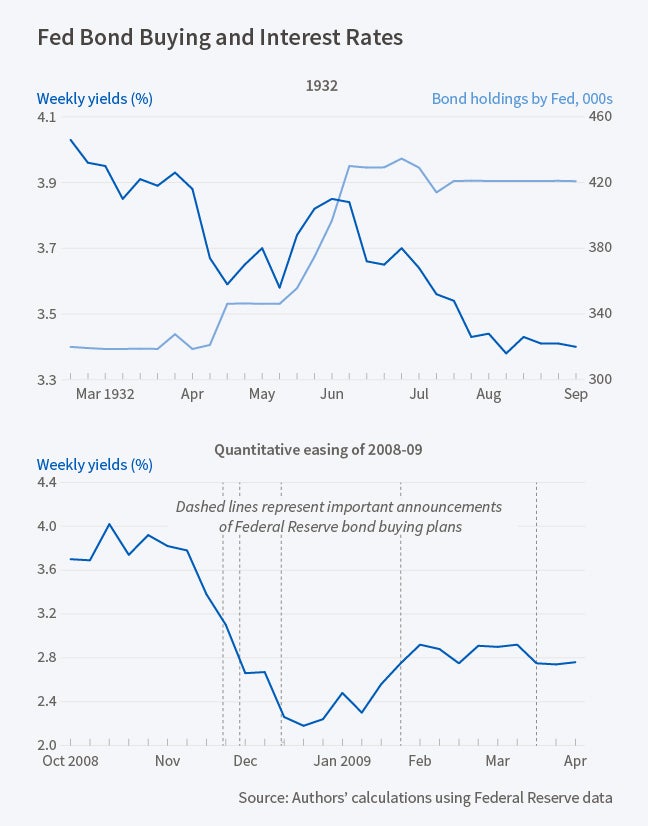
Outside the box. By law the Fed implements monetary policy for the US. In addition to its forward guidance the Fed pursued two other types of nontraditional policy actions during the Great Recession. A fter the Federal Reserve effectively slashed interest rates to zero in response to the Great Recession some doubted that there was much else it could do to accelerate the pace of recovery. The Feds approach to dealing with. Monetary policy involves manipulating the available money supply in the country.