
Michaelis Menten Approach To Enzyme Kinetics. It takes the form of an equation relating reaction velocity to substrate concentration for a system where a substrate S binds reversibly to an enzyme E to form an enzyme-substrate complex ES which then reacts irreversibly to generate a product P and to regenerate the free enzyme E. The convention used for this slides is to use UPPERCASEfor the. Michaelis-Menten Kinetics Introduction. What is MichaelisMenten kinetics model.
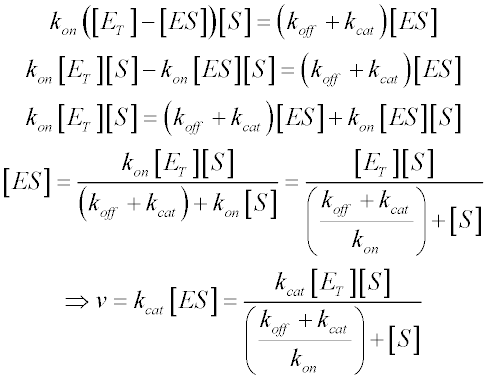
It is a pseudoequilibrium constant signifying the concentration of substrate at halfmaximal velocity of the enzyme. It takes the form of an equation relating reaction velocity to substrate concentration for a system where a substrate S binds reversibly to an enzyme E to form an enzyme-substrate complex ES which then reacts irreversibly to generate a product P and to regenerate the free enzyme E. The enzyme interacts with the substrate by binding to its active site to form the enzyme-substrate. When the inhibitor is a non-competitive inhibitor the situation is more. The Michaelis-Menten model 1 is the one of the simplest and best-known approaches to enzyme kinetics. Condition that assumes that the rate at which the enzyme and the substrate associate to form enzymesubstrate complex k 1 ES is the same as the rate at which the latter dissociates back to its individual components k 1 ES.
When this is a competitive inhibitor only the waiting time is modified demonstrating that this compound binds at the same site as substrate.
An introduction to enzyme kinetics and the Michaelis-Menten plot the significance of Vmax and Km as well as the significance of pH and temperature on enzym. This includes the effect of temperature and pH on enzymatic activity. The Michaelis-Menten equation has been widely used for over a century to estimate the enzyme kinetic parameters from reaction progress curves of substrates which is. This original approach to Michaelis-Menten kinetics also permits a simple visualization of the events taking place at the recognitionbinding site of an enzyme when inhibitor is present. It takes the form of an equation relating reaction velocity to substrate concentration for a system where a substrate S binds reversibly to an enzyme E to form an enzyme-substrate complex ES which then reacts irreversibly to generate a product P and to regenerate the free enzyme E. MichaelisMenten kinetic parameters of immobilized enzymes can be determined using the same general approaches developed for the study of solubilized enzymes.