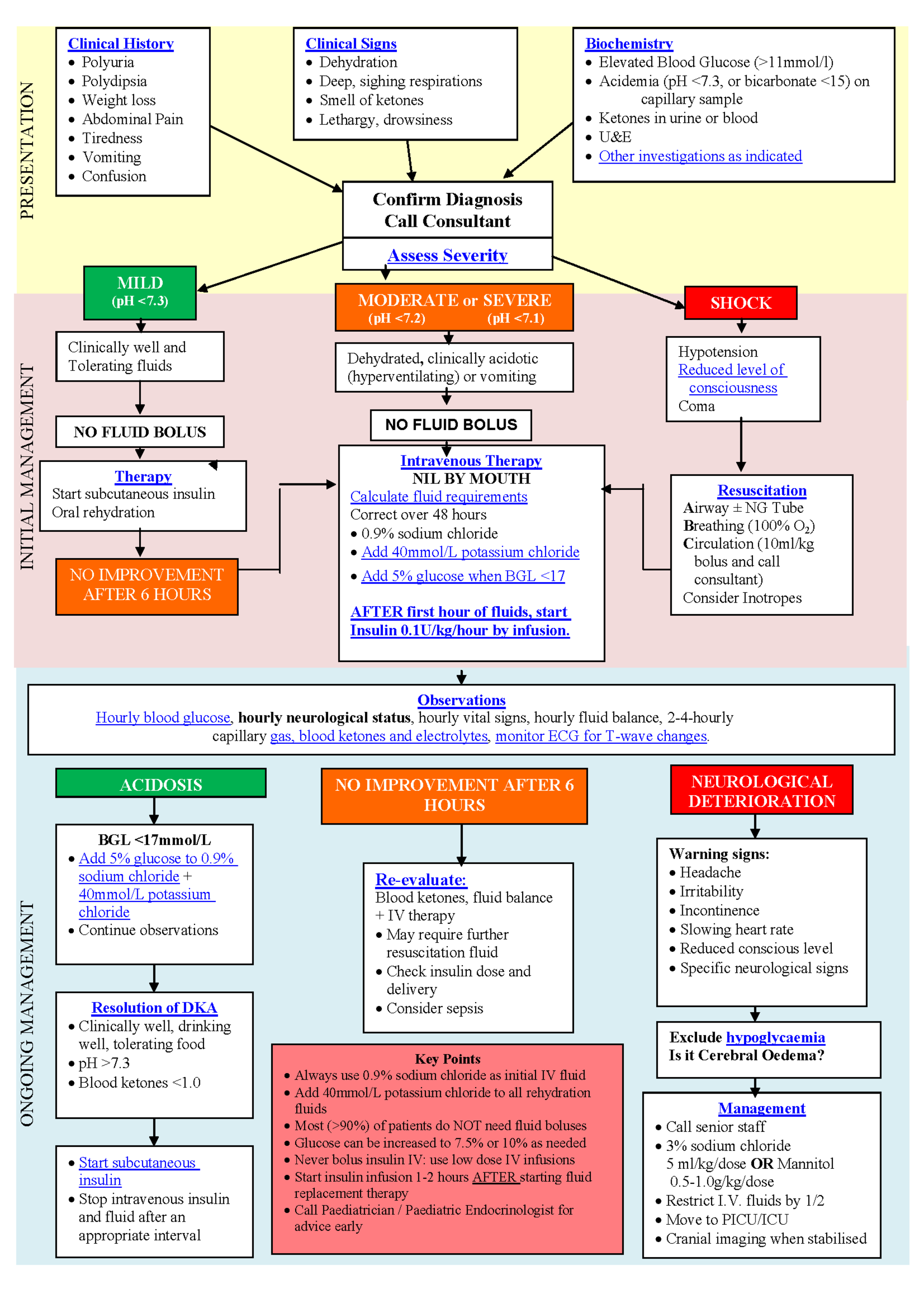
Management Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis In Children. 1Department of Paediatrics and Child Health Muhimbili National Hospital PO. Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is a life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus. Ketoacidosis in children and adolescents with diabetes. The rates of mortality and permanent neurologic.
Am J Emerg Med. In a child with established diabetes whose parents have been trained in sick day management hyperglycemia and ketosis without vomiting or severe dehydration can be managed at home or in an outpatient health care facility eg emergency ward provided an experienced diabetes team supervises the care 31 33. Diabetic ketoacidosis is a common presentation of both T1DM and T2DM in children and adolescents. The object of this review is to provide the definitions frequency risk factors pathophysiology diagnostic considerations and management recommendations for diabetic ketoacidosis DKA in children and adolescents and to convey current knowledge of the causes of permanent disability or mortality from complications of DKA or its management particularly the most common complication cerebral. The following may help decrease your childs risk for DKA. Majaliwa ES1 Mohn A Chiavaroli V Ramaiya K Swai AB Chiarelli F.
Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in children with type 1 diabetes with a case fatality rate ranging from 015 to 031 percent in the United States and other resource-rich countries DKA also can occur in children with type 2 diabetes.
Check his or her blood sugar levels often. Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is a life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus. Am J Emerg Med. Cerebral edema is the most frequent serious complication of diabetic ketoacidosis DKA in children occurring in 1 to 5 of DKA episodes. Initial fluid resuscitation should be with an isotonic solution. Subsequent fluid management should be with a solution that has a tonicity of at least 045 saline.
