
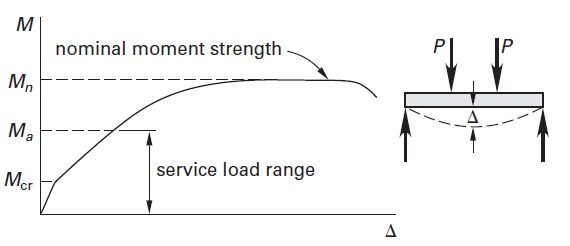
Inelastic Behaviour Of Concrete Beams. The specimens were subjected to inelastic cyclic loading. Here the concrete is well into the inelastic range although the steel has not yielded. FEMA 451B Notes Inelastic Behavior 6-2 Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451 Design Examples Inelastic Behaviors 6 - 2 Illustrates inelastic behavior of materials and structures Explains why inelastic response may be necessary Explains the equal displacement concept Introduces the concept of inelastic design response spectra. 1 elastic attaining of initial yield surface.
Precast concrete frame construction in Mexico relies heavily on two types of beam-column connections. During inelastic deformations the actual material properties are beyond elastic range and hence damages in these regions are obvious. Plasticity of reinforcement is also considered. The inelastic behavior of concrete is defined by a uniaxial stress-strain curve with postpeak softening in compression and a zero strength in tension. The experimental results from tests of four beam-column subassemblies constructed with high-strength concrete f c 9500 psi 65 MPa are presented and the results compared with the response of a specimen constructed with ordinary-strength concrete. Some important aspects of behavior of the beams having different tensile reinforcement.
Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers.
The ends of the beams act as hinges undergoing inelastic rotation with no change in mo-ment the moment stays constant at -40 units. The neutral axis depth c 1 is less than the elastic kd and is changing with inc reasing load as the shape of the concrete stress distribution changes and the steel stress changes. In reinforced concrete members the inelastic rotations spread over definite regions called as plastic hinges. In this case precast concrete columns several stories high are constructed leaving windows in the columns at the floor levels. 2 perfect plastic flow in the limited range of deformation. The results of an investigation into the behaviour of reinforced concrete members sub-jected to cyclic loading in the inelastic range are summarizedo The investigation comm-ences with studies of the Bauschinger effect for cyclically stre ssed mild steel reinforce-ment and the influence of rectangular steel hooping on the stress-strain behaviour of concre te o Using the se derived stress-strain curves the.