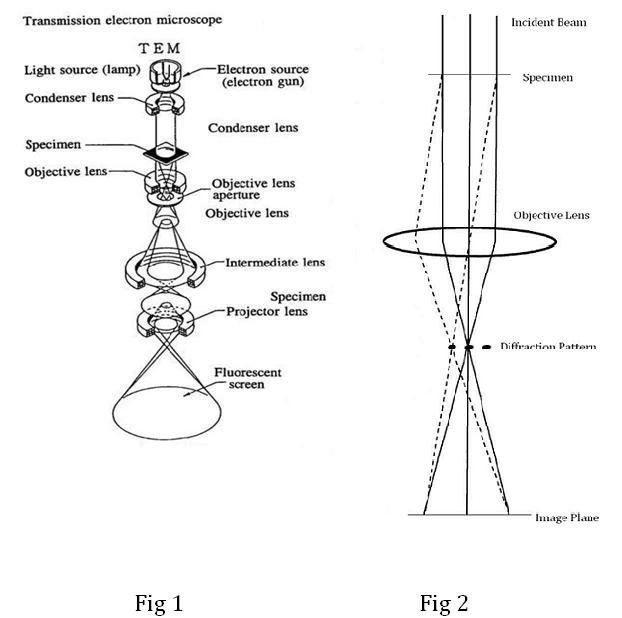
In A Transmission Electron Microscope The Lenses Are. Phosphorescent screen-The screen at the bottom of the electron column where the specimen is viewed. Projector lens-The final lens in a TEM. This stream is confined and focused using metal apertures and magnetic lenses into a thin focused monochromatic beam. The selected area electron diffraction SAED aperture Ap and the sample or speciment Spec are indicated as well as the objective Obj and projector Proj or condenser Cond lenses.

The TEM uses two condenser lenses to converge the beam of electrons to the specimen. Interactions occur inside the irradiated sample affecting the electron beam. Ernst Ruska later received Nobel Prize for his work in 1986. Electron microscopes use shaped magnetic fields to form electron optical lens systems that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope. Ray diagram of a conventional transmission electron microscope top path and of a scanning transmission electron microscope bottom path. This is an image of the copper coil of an electromagnetic lens from an electron microscope.
This stream is confined and focused using metal apertures and magnetic lenses into a thin focused monochromatic beam.
Ray diagram of a conventional transmission electron microscope top path and of a scanning transmission electron microscope bottom path. It consists of an electron gun to produce electrons. Used to assist in magnifying the image and to project the magnified image onto the phosphorus screen. A Transmission Electron Microscope functions under the same basic principles as an optical microscope. Phosphorescent screen-The screen at the bottom of the electron column where the specimen is viewed. Electron microscopes use shaped magnetic fields to form electron optical lens systems that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope.