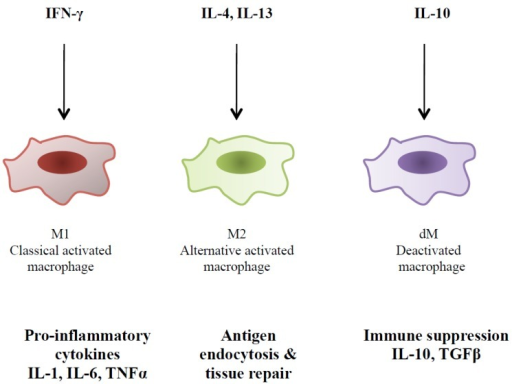
Il 4 Anti Inflammatory Cytokine. Hence the delivery of these microspheres in an OA joint can attenuate the stimulation of chondrocytes and the resulting secretion of catabolic factors such as. Cytokine-mediated processes such as the activation of T helper 2 cells by IL-4 and IL-13 the resolution of inflammation by IL-9 IL-5-induced eosinophil expansion IL-33-mediated macrophage polarization the production of IL-10 by regulatory B cells and IL-27-mediated suppression of lymphoid follicle formation are all involved in governing the regulation and resolution of inflammation in RA. However its mechanisms of action remain poorly understood. It was observed that the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α IL-4 and IL-1β in skin lesion decreased in response to treatment with diosmetin.
Hence the delivery of these microspheres in an OA joint can attenuate the stimulation of chondrocytes and the resulting secretion of catabolic factors such as. Major anti-inflammatory cytokines include interleukin IL-1 receptor antagonist IL-4 IL-10 IL-11 and IL-13. The aim of this paper is to review the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 and their receptor signals. The anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 IL-6 IL-10 and IL-13 inhibit the synthesis of IL-1β yet they stimulate the synthesis of IL-1ra. In addition the anti-inflammatory effect of diosmetin was evaluated in LPS- or IL-4-induced a mouse macrophage cell line raw 2647. Major anti-inflammatory interleukins include interleukin IL-1 receptor antagonist IL-4 IL-6 IL-10 IL-13 IL-19 and IL-35.
In addition the anti-inflammatory effect of diosmetin was evaluated in LPS- or IL-4-induced a mouse macrophage cell line raw 2647.
Here we show that IL-10 opposes the switch to the metabolic program induced by inflammatory stimuli in macrophages. Major anti-inflammatory cytokines include interleukin IL-1 receptor antagonist IL-4 IL-6 IL-10 IL-11 and IL-13. Diosmetin inhibited the production of nitric oxide and decreased the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase iNOS. Early secretion of IL-4 leads to polarization of Th. IL-10 signals through a receptor complex consisting of two IL-10 receptor-1 and two IL-10 receptor-2 proteins. IL-10 binding induces STAT3 signalling via the phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic tails of IL-10 receptor 1 IL.