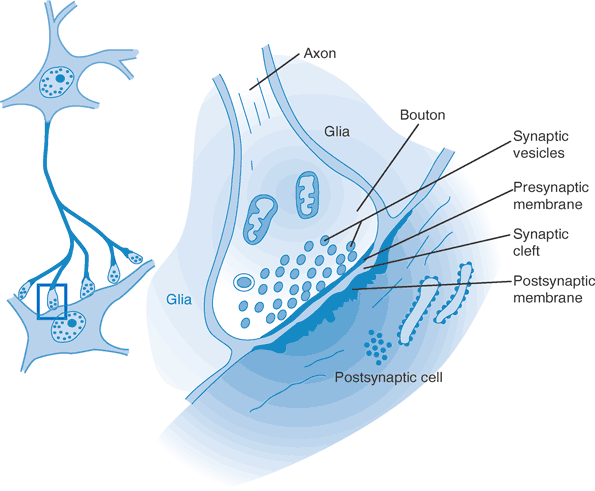
Gamma Aminobutyric Acid Appears To Decrease Synaptic Transmission. It also was 3 years before modern molecular biology was begun by Watson and Crick Watson and Crick 1953. Alan Bown Brock University Biology Science Department 600 Glenridge Ave St. GABA-induced responses were antagonized by picrotoxin and were insensitive to bicuculline or strychnine. GABAs natural function is to reduce the activity of the neurons to which it binds.
GABA Gamma-aminobutyric acid study guide by araceliboss includes 4 questions covering vocabulary terms and more. In the larger fibers which have low input resistance the decrease may disappear within 2 min. The role of gamma-aminobutyric acid GABA-benzodiazepine neurotransmission in an animal model of methamphetamine-induced psychosis Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi. Expert answeredJanet17Points 45182 Log in for more information. It look as if to decrease synaptic transmission and is actually used in drugs called GABAergic drugs or GABA analogues. GABA-induced responses were antagonized by picrotoxin and were insensitive to bicuculline or strychnine.
The role of gamma-aminobutyric acid GABA-benzodiazepine neurotransmission in an animal model of methamphetamine-induced psychosis Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi.
9 There is also evidence that GABA acts as a trophic factor during brain development. Quizlet flashcards activities and games help you improve your grades. Gamma-aminobutyric acid appears to decrease synaptic transmission and seem related to drugs. It derives from a butyric acid. Gamma-aminobutyric acid is a gamma-amino acid that is butanoic acid with the amino substituent located at C-4. Neurotransmitters function as chemical messengers.
