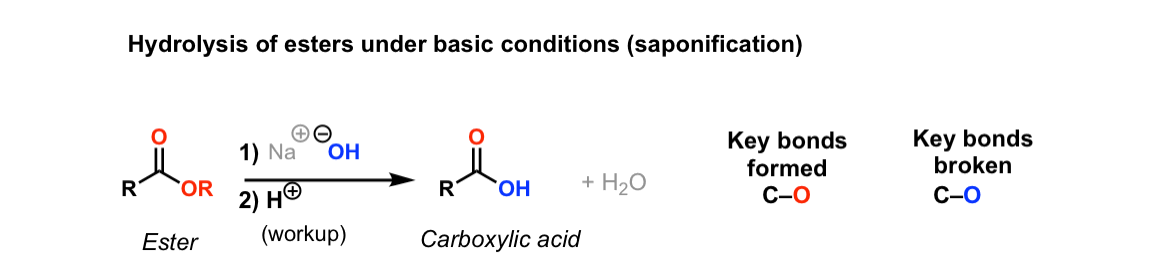
Base Hydrolysis Of Ester. In principle these reactions are reversible and both reactions canbe catalysed either by acids or bases. Technically hydrolysis is a reaction with water. Esters are hydrolyzed by strong alkalis such as NaOH aq or KOH aq. The hydroxide nucleophiles attacks at the electrophilic C ofthe ester CO breaking the π bond and creating the tetrahedral intermediate.
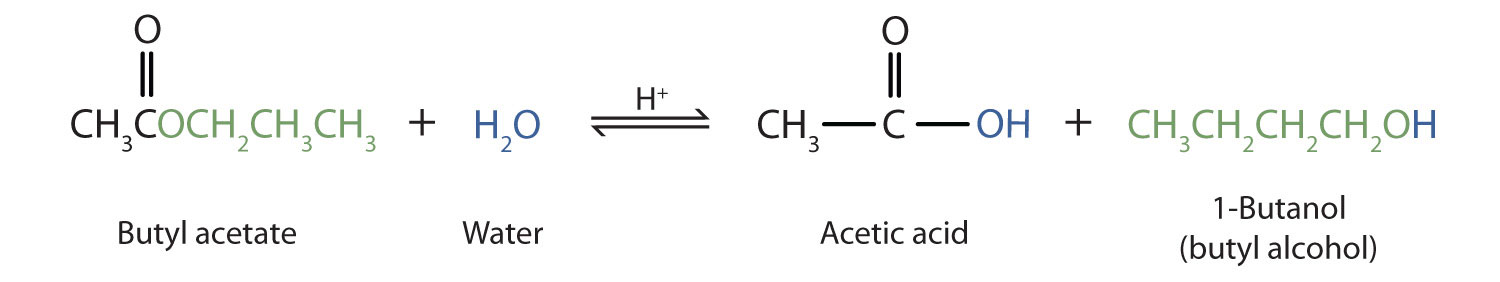
That is exactly what happens when esters are hydrolysed by water or by dilute acids such as dilute hydrochloric acid. This method conveniently provides both carboxylic acids and alcohols from the corresponding esters and sodium hydroxide in a few minutes at room temperature. Ester Hydrolysis The splitting of an ester into the component acid and alcohol isknown as ester hydrolysis. Mechanism of Base Hydrolysis of Esters. Ester is heated in reflux with dilute hydrochloric acid dilute acid. The 2-aminobenzoate esters hydrolyze with similar rate constants in the pH-independent reactions and these water reactions are 2-fold slower in D 2 O than in H 2 O.
The most likely mechanism involves intramolecular general base catalysis by the neighboring amine group.
The ester is heated with a large excess of water containing a strong-acid catalyst. The hydrolysis of ester is commonly performed with acid or base Koshikari 2012. Basic hydrolysis of the ester is called saponification because this reaction produces soaps Latin word sapo means soap. A general procedure for the base-promoted hydrolysis of hindered esters at ambient temperatures. A very mild and rapid procedure for the efficient alkaline hydrolysis of esters in non-aqueous conditions has been developed by the use of dichloromethanemethanol 91 as solvent. In basic hydrolysis the molecule of the base splits the ester linkage.