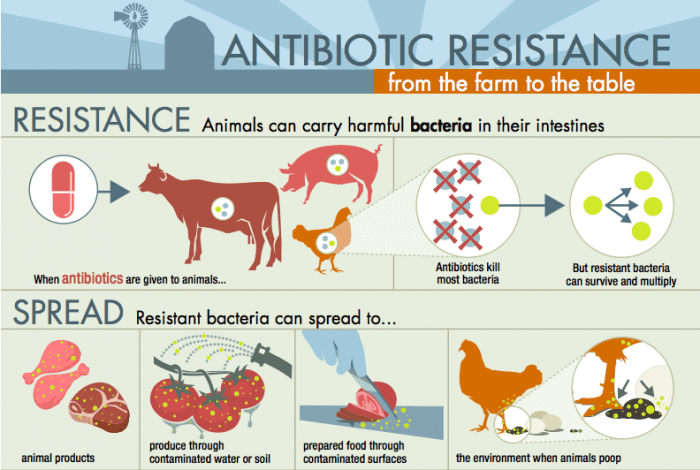
Antibiotic Resistance In Agriculture. Antibiotic Resistance and Food Animals like people carry bacteria germs in their gut which can include antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Therefore intrinsic resistance to antibiotics is a desirable trait for the rhizobial population. It increases the rhizobias chances of growth multiplication and persistence in the soil. Overuse of antibiotics has accelerated the development and dissemination of antibiotic resistant bacteria ARB and antibiotic resistance genes ARGs.
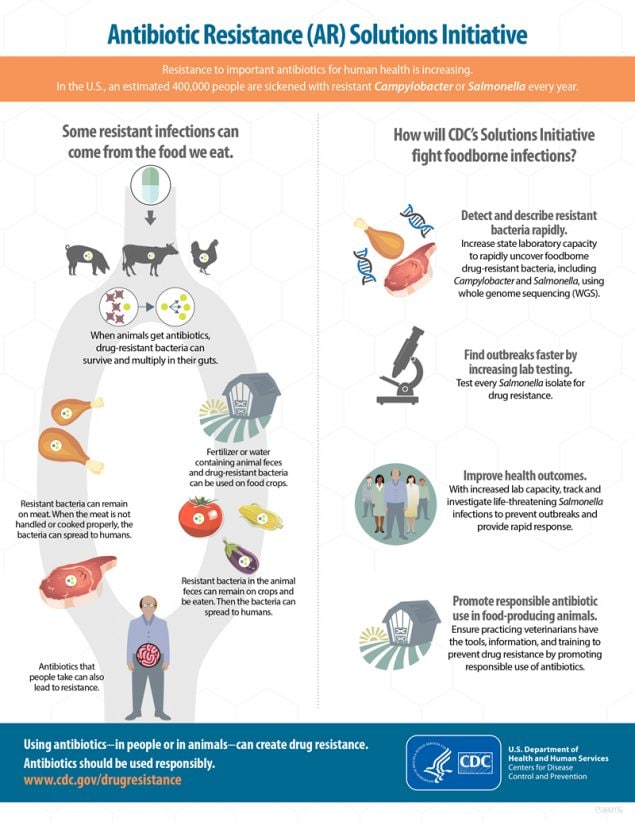
The significance of agricultural antibiotics in the emergence and spread of clinical antibiotic resistance is a matter of ongoing debate and controversy with one prominent commentary asserting albeit without support or citation that farming practices are largely to blame for the rise of antibioticresistant strains Kennedy 2013. A team of researchers at Iowa State University were recently awarded a 1 million grant from USDAs National Institute of Food and Agriculture to study how technologies can decrease development of those bacteria. As defined by the World Health Organization Antimicrobial resistance AMR is resistance of a microorganism to an antimicrobial drug that was originally effective for treatment of infections caused by it. Antibiotic resistance genes which are known to compromise antibiotic therapy and are present on MGE in pathogens are categorized in the highest. Abstract The use of antibiotics in animal agriculture has exacerbated the presence of both antibiotic resistance genes ARGs and residual antibiotics. 4 rows Antibiotic consumption and development of antibiotic resistance in agriculture Antibiotics are.
Every year in the US antibiotic-resistant bacteria infect up to 28 million people and are responsible for more than 35000 deaths.
As defined by the World Health Organization Antimicrobial resistance AMR is resistance of a microorganism to an antimicrobial drug that was originally effective for treatment of infections caused by it. This type of bacteria is resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance genes detected in this way have been ranked recently into seven categories of the resistance readiness condition Rescon which is defined by the risk of acquiring and conferring ABR to human pathogens. Soil is an essential part of our ecosystem and plays a crucial role as a nutrient source provides habitat for plants and other organisms. Coli bacteria One of the most well-known resistant bacteria is MRSA that occurs in humans as well as animals. With a large population of rhizobia in the soil infectivity of host plants and the subsequent BNF efficiency can be guaranteed.