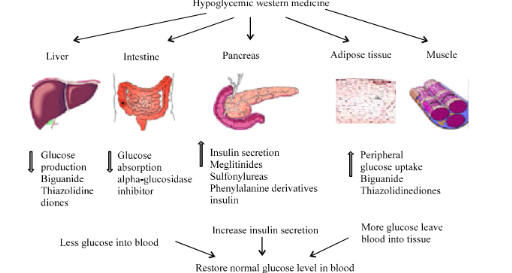
Alpha Amylase Inhibitor Diabetes. The optimum pH for the inhibitor is 45 to 55 and the optimal temperature is 22 to 37C. α-Amylase Inhibitors α-Amylase inhibitors inhibit the activity of salivary and pancreatic amylase in vitro and in vivo. The alpha amylase inhibitor prevents starch digestion by completely blocking access to the active site of the alpha-amylase enzyme. α-Amylase enzyme plays a key role in the onset of the abnormal condition by breaking starch into glucose.
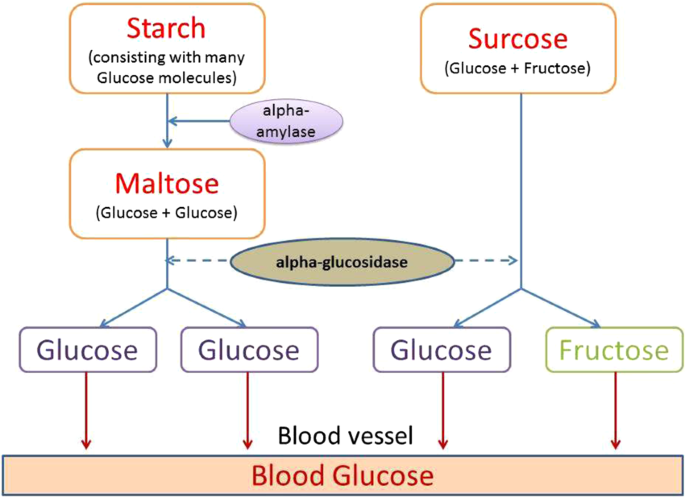
Basically alpha-amylase inhibitors are classified into two groups. Factors that affect the activity of the alpha-AI isoform inhibitor are pH temperature incubation time and the presence of particular ions. Acarbose a well-known and efficacious alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase inhibitor is a post-prandial acting anti-diabetic drug. Thus the inhibitors of both α-amylase which breaks down long-chain carbohydrates and α-glucosidase which catalyses the cleavage of glucose from disaccharide are effective in delaying glucose absorption. There is no activity at 0C and the inhibitor is. The studies on α-amylase inhibitors have been done on the broad range of research.
α-Amylase Inhibitors α-Amylase inhibitors inhibit the activity of salivary and pancreatic amylase in vitro and in vivo.
They can impair the growth and metabolism of animals when given at high levels in the diet but may have beneficial uses in treatment of obesity or diabetes. From this point of view more researchers have focused on the search for more effective inhibitors of anti-diabetic. The α-amylase inhibitors act as an ant nutrient that control rate of digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. Also potentially become useful in control of obesity and diabetes. There is no activity at 0C and the inhibitor is. Diabetes mellitus is the most widespread disorders prevalent in current period.